Content
- Introduction
- REST Concepts
- Postman
- Creating API Project
- Directory Structure
- HTTP Verbs
- Create Model and API Controller
Introduction
- An API (Application Programming Interface) is a contract that lets one piece of software talk to another over a network. In web development an API usually exposes HTTP endpoints that accept requests (JSON, form data, etc.) and return responses (JSON, status codes).
- Think of an API as the waiter in a restaurant — the client (app/website) places an order, the waiter sends that order to the kitchen (server/DB), and brings back the result.
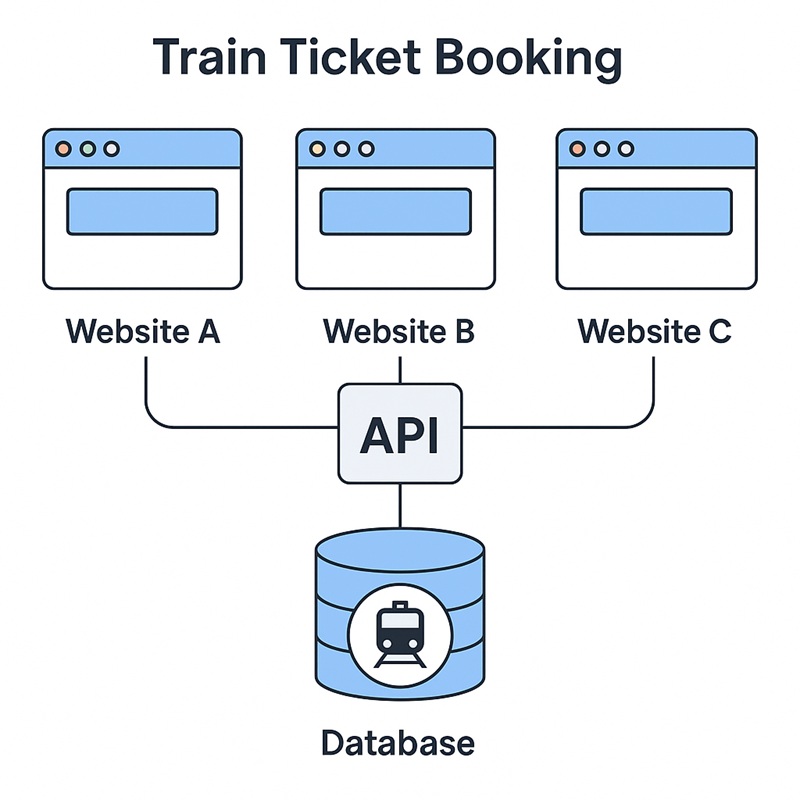
- The image illustrates how multiple websites can access the same train ticket database using a central API. Even though users book tickets from different platforms, all platforms connect to a single backend system.
- This avoids duplicate bookings and keeps seat availability accurate.
REST Concepts
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style used to design scalable and lightweight web services. ASP.NET Web API is built on REST principles.
| REST Concept | Short Description |
|---|---|
| Statelessness | The server does not store client session; each request must contain all required information. |
| Resource-Based | Everything is treated as a resource and accessed using unique URLs, like users, products, or bookings. |
| Uniform Interface | Uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for communication, making APIs predictable. |
| Representation of Resources | Resources are returned in formats like JSON or XML, independent of internal server structure. |
| Client–Server Separation | The client handles UI; the server handles data and logic, keeping both independent. |
| Cacheable | Responses can be cached to improve performance and reduce load on the server. |
| Layered System | API may have multiple layers (load balancers, gateways), but clients interact with it as a single unit. |
Postman
- Postman is a powerful API testing tool used by developers to interact with APIs without writing any code.
- Postman is extremely useful when building Web APIs, because you can test your API endpoints directly without creating any frontend UI.
- Download Postman
Creating API Project
- Open Visual Studio -> Create New Project -> ASP.NET Core Web API -> Enter Project Name and Select Location -> Create
- Run Project and test default API with Postman and Swagger
Directory Structure
- Connected Services – Integrations registered in the project (Azure services, external REST/gRPC services, WSDL/WCF references). Visual Studio can scaffold clients and configuration from these entries.
- Dependencies – NuGet packages, SDK references, and project references required by the application. Use this to view or update library versions and package metadata.
- Properties – Project-level configuration files. The key file here is
launchSettings.json, which defines run profiles, environment variables, and local URLs used during development. - Controllers/ – API controllers that define HTTP endpoints (actions mapped to GET/POST/PUT/DELETE). Controllers coordinate request validation, call services, and return HTTP responses.
- Models/ – POCO classes representing domain entities and DTOs used by the API (e.g., Train, Seat, Booking, CreateBookingDto). Models define the shape of data persisted and transferred.
- projectname.http – A plain text file with HTTP requests (requests + headers + bodies) used inside Visual Studio / VS Code REST client to quickly test endpoints without Postman.
- appsettings.json – Central configuration file for connection strings, API keys, logging levels, feature flags, and environment-specific settings (use appsettings.Development.json for overrides).
- Program.cs – Application entry point (in .NET 6+). Registers services (DbContext, DI services, authentication, Swagger), configures middleware (routing, CORS, error handling), and starts the web host.
HTTP Verbs
HTTP verbs (also called HTTP methods) define the action a client wants to perform on a resource in a Web API. RESTful APIs heavily rely on these verbs to indicate operations like fetching, creating, updating, or deleting data.
| HTTP Verb | Purpose | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Retrieve data | Fetch items or a single record |
| POST | Create new data | Add a new record to the server |
| PUT | Update entire record | Replace an existing item |
| PATCH | Partial update | Modify specific fields |
| DELETE | Remove data | Delete a record |
Create Model and API Controller
Class File: Product Model
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
}Add API Controller
Right click on Controller folder -> Add -> Controller -> Select API -> API Controller - Empty ->Add